Edit data and create datasets you can share.
A filter only shows entries with values that match the filter. So if you are working with a large dataset you can focus on a subset of the dataset.
A quick filter is a simple way to search and will look in every column. For instance, to look for information about “Sal”:
<Enter> .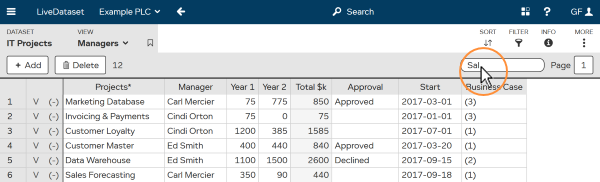
In this example, “Sal” was found in 2 entries:
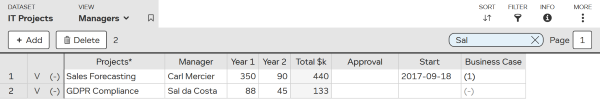
To remove the quick filter:
TIP A quick filter should not be used on large datasets. Read performance for more information and alternatives to try.
As you are working with organized data you will normally want to filter within a specific column e.g. finding projects where “Approval” column = “Approved”.
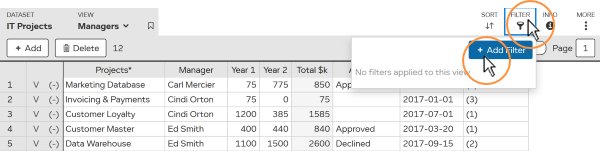
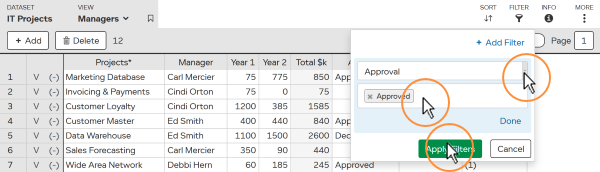
Depending on the column type, you have different comparisons to choose from e.g. “>”
To change a filter:
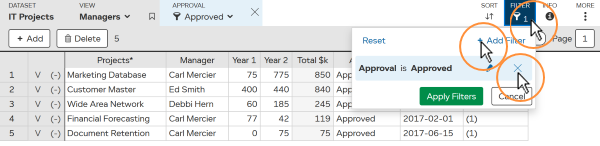
You can use multiple filters simultaneously. Only entries that match all the filters will be shown.
e.g (Year 1 > 100 ) AND (Year 2 > 100 ) AND (Manager = Ed Smith)
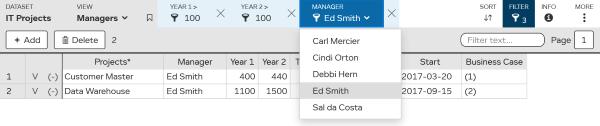
TIP When you use a filter on a list column, you can use dropdown to select another value.
Filters you add are automatically saved and will be there when you return to this view. See bookmark for more information.
You can also save and name your filters. See bookmark for more information.
Selectors act like filters, but they are configured for you by the dataset designer. See selectors for more information.
Below a dataset designer has created a selector on the “Manager” column.
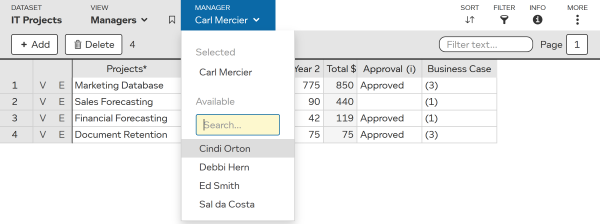
TIP You can tell this is a selector and not a filter, as filters are shown with a and a to close the filter.